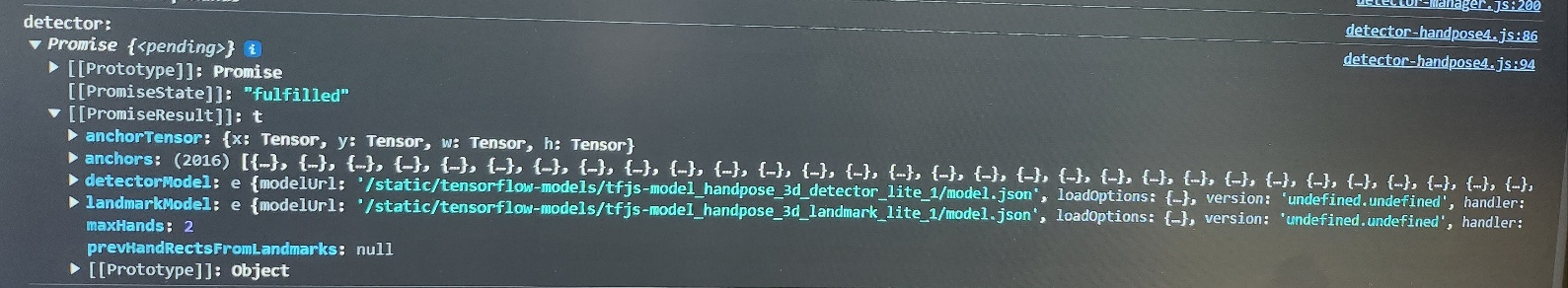
개요
- 이번 프로젝트에서는 ①클래스를 상속 받아 기능 확장하여, ②Tensorflow-models 모델의 전형적인 구조에 따라 핵심 코드를 작성하였음
- 상속
- 의미 : 부모 클래스의 프로퍼티, 메서드를 자식 클래스가 물려받는 것
- 기능 : 부모 클래스 기능을 자식 클래스에서 확장시킬 수 있음.
- ES6 모듈 개발 전 : 프로토타입 체인 방식으로 상속, 그러나 이는 가독성 떨어짐.
- ES6 모듈 개발 후 : Class + extends 키워드를 사용하여 상속, 상속하는 것 확실히 티 낼 수 있게 됨
- 이번 프로젝트에서의 상속
- Detector 클래스
class Detector {
constructor () { }
// 그 외 내용: 자바스크립트에서의 getter and setter
// https://ko.javascript.info/property-accessors
static get DIMENSIONS () { //
return [480, 360];
}
enable () {
this._enable = true;
}
disable () {
this._enable = false;
this._result = null;
}
detect (imageData) { }
isExistContent (result) {
return result && result.length > 0;
}
draw (canvas) { }
}
module.exports = Detector;
- HandposeDetector 클래스
class HandposeDetector extends Detector {
constructor() {
super();
this._result;
}
enable() {
super.enable();
this._canvas = document.createElement("canvas");
this._canvas.width = Detector.DIMENSIONS[0];
this._canvas.height = Detector.DIMENSIONS[1];
this._context = this._canvas.getContext("2d");
}
disable() {
super.disable();
delete this._context;
delete this._canvas;
this._context = null;
this._canvas = null;
}
_createDetector() {
const model = SupportedModels.MediaPipeHands;
const detector = createDetector(model, {
runtime: "tfjs",
modelType: "lite",
maxHands: 2, // or 2~10.
flipHorizontal: false,
staticImageMode: false,
detectorModelUrl:
"/static/tensorflow-models/tfjs-model_handpose_3d_detector_lite_1/model.json",
landmarkModelUrl:
"/static/tensorflow-models/tfjs-model_handpose_3d_landmark_lite_1/model.json",
});
console.log("model loading success!, detector: ", this._detector);
return detector;
}
detect(imageData) {
if (!this._detector) {
this._createDetector().then(detector => {
this._detector = detector;
console.log("model loading success!, detector: ", this._detector);
})
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
this._detector.estimateHands(imageData).then(result => {
this._result = result;
console.log(`this._result: `, this._result);
this._result.forEach((res) => {
console.log(`${res.handedness} hand keypoints:`);
res.keypoints.forEach((keypoint, i) => {
let x = keypoint.x - 320;
let y = keypoint.y - 240;
console.log(`Keypoint ${i}: [${x}, ${y}]`);
})
})
resolve(this._result);
}).catch(e => {
reject(e);
});
})
}
/**
중략
**/
}
module.exports = HandposeDetector;
개념 정리
출처 : https://ko.javascript.info/class-inheritance
1. class와 prototype
- 부모 클래스 Animal과 객체 animal
class Animal {
constructor(name) {
this.speed = 0;
this.name = name;
}
run(speed) {
this.speed = speed;
alert(`${this.name} 은/는 속도 ${this.speed}로 달립니다.`);
}
stop() {
this.speed = 0;
alert(`${this.name} 이/가 멈췄습니다.`);
}
}
let animal = new Animal("동물");- 객체 animal과 클래스 Animal의 관계
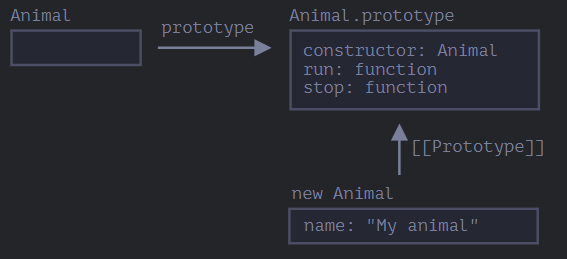
- Animal vs Animal.prototype
Animal : Class Definition Animal.prototype : Prototype-Based Definition class 키워드로 정의한 클래스 객체의 프로토타입을 확장하여 메서드와 속성을 추가한 것 ES6 이후 문법 ES6 이전 문법 클래스 = 메서드(run, stop) + 속성(speed, name) 클래스는 생성자(constructor)를 가질 수 있음 - constructor
- 함수 자신, 따라서 위 그림에서 constructor : Animal 로 표시됨
(∵ 자바스크립트에서 클래스⊂함수, 클래스는 생성자 함수로써 내부적으로 생성자 함수와 프로토타입을 생성하기 때문) - 만약 Animal 함수의 프로퍼티 ‘prototype’에 constructor 객체 하나만 있다면 ‘디폴트 프로퍼티가 있다’고 표현 가능
(디폴트 프로퍼티 : 개발자가 별도로 할당하지 않아도 기본적으로 가지는 프로퍼티) - 기능적으로 클래스에서 객체를 생성하고 초기화하기 위해 사용하는 메서드라고 볼 수 있음. 클래스를 통해 새로운 객체를 생성할 때 자동 호출됨
- 함수 자신, 따라서 위 그림에서 constructor : Animal 로 표시됨
- constructor
2. extends키워드로 상속 받기
- 자식 클래스 Rabbit
class Rabbit extends Animal {
hide() {
alert(`${this.name} 이/가 숨었습니다!`);
}
}
let rabbit = new Rabbit("흰 토끼");
rabbit.run(5); // 흰 토끼 은/는 속도 5로 달립니다.
rabbit.hide(); // 흰 토끼 이/가 숨었습니다!- 클래스 Rabbit을 이용하여 만든 객체 rabbit
: rabbit은 rabbit.hide() 로 Rabbit 클래스의 메서드에도, rabbit.run() 으로 Animal의 메서드에도 접근 가능 - extends는 프로토타입을 기반으로 동작
- 따라서 extends는 Rabbit.prototype.[[Prototype]] 을 Animal.prototype으로 설정함
- Rabbit.prototype에서 메서드를 찾지 못하면 Animal.prototype에서 메서드를 가져옴
- 프로젝트에 적용
class HandposeDetector extends Detector { }
3. 메서드 오버라이딩(Method Overriding) : super 키워드 활용
- 의미 : 부모 클래스의 메서드를 재정의하여 자식 클래스에서 사용하는 것
→ 재정의 : 일부 기능만 변경 or 기능 확장 - super 키워드 활용
- super(…) : 부모 생성자 자체 호출, 따라서 자식 생성자 내부에서만 사용 가능
- super.method명(…) : 부모 클래스의 method를 호출
- 핵심 코드 : 부모 클래스의 stop() method를 오버라이딩한 rabbit.stop() 정의
class Rabbit extends Animal {
hide() {
alert(`${this.name}가 숨었습니다!`);
}
stop() {
super.stop(); // 부모 클래스의 stop을 호출해 멈추고,
this.hide(); // 숨습니다.
}
}
let rabbit = new Rabbit("흰 토끼");
rabbit.run(5); // 흰 토끼가 속도 5로 달립니다.
rabbit.stop(); // 흰 토끼가 멈췄습니다. 흰 토끼가 숨었습니다!- 프로젝트에 적용
enable() {
super.enable();
this._canvas = document.createElement("canvas");
this._canvas.width = Detector.DIMENSIONS[0];
this._canvas.height = Detector.DIMENSIONS[1];
this._context = this._canvas.getContext("2d");
}
4. 생성자 오버라이딩(Constructor Overriding)
- 의미 : 부모 클래스의 생성자를 재정의하여 자식 클래스에서 사용하는 것
- super 키워드 활용
- super 키워드가 상속 클래스의 생성자 함수가 실행되면, 부모 클래스의 생성자가 ①빈 객체를 만들고 ②this에 이 객체가 할당되도록 함
- 따라서 super 키워드가 없으면 this가 될 객체가 생성되지 않아 자식 클래스 생성자 실행 시 오류 발생함
- 핵심 코드
class Rabbit extends Animal {
constructor(name, earLength) {
super(name);
this.earLength = earLength;
}
// ...
}- 프로젝트에 적용
class HandposeDetector extends Detector {
constructor() {
super();
this._result;
}
}
배운점 (요약)
- 이번 프로젝트에서는 ①클래스를 상속 받아 기능 확장하여, ② Tensorflow-models 모델의 전형적인 구조 에 따라 핵심 코드를 작성하였음
- 실제 코드를 작성할 때는 정확히 무슨 뜻인지 모르고, 용례를 보고 이런 느낌이구나 라고 생각하며 사용했음
- 그러나 프로젝트를 마무리하며 개념 정리를 하니, 밑그림만 있던 것이 구체적인 채색까지 되는 느낌이었음. 따라서 향후 활용할 수 있는 자신감이 생겼음. 또한 효율적, 효과적인 코드를 위해 상속 및 오버라이딩은 필수 요소라고 생각했음.
'Backend > Node.js' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Coding-Practice] 코드 최적화 - 2. 유효성 검사 (0) | 2023.11.30 |
|---|---|
| [Coding-Practice] 코드 최적화 - 1. this.~ (1) | 2023.11.30 |
| [Function] 프로젝트 내에서 함수 구분 (1) | 2023.11.30 |
| [Setting] npm link 2 (0) | 2023.11.30 |
| [Setting] Node.js, npm 버전 업데이트 (0) | 2023.10.18 |